The Theta Sketch definition enables a uniform and simplified approach to performing the three standard set operations, Union (∪), Intersection (∩) and Difference (\).
The diagram below illustrates how the Intersection operation can be performed by examining the internal hash values (entries) of both sketches, A and B. Note that the result of a simple 2-way set operation is another sketch! Performing Union and Difference operations are similar. The equations for all three set operations are generalized below where the delta symbol, Δ, represents one of the three set operations.
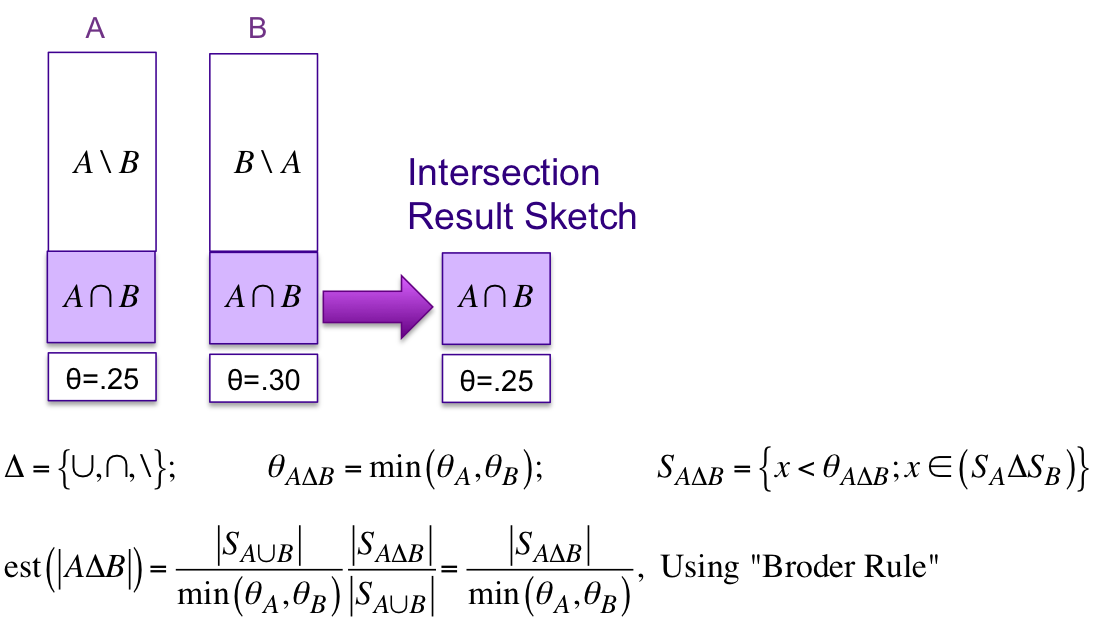
The fact that set operations produce sketches as results enables full set expressions, such as
((A ∪ B) ∩ (C ∪ D))\(E ∪ F).
The Union and Intersection operations are symmetric (i.e., sketch order insensitive) and naturally iterative. The AnotB operation, however, is asymmetric (i.e., sketch order sensitive) and not iterative.
This is a Java example of all three operations:
import static org.testng.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class SetOpsExample {
int k = 4096;
UpdateSketch skA = Sketches.updateSketchBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).build();
UpdateSketch skB = Sketches.updateSketchBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).build();
UpdateSketch skC = Sketches.updateSketchBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).build();
@Test
public void check() {
for (int i=1; i<=10; i++) { skA.update(i); } //{1,2,...,10}
for (int i=1; i<=20; i++) { skB.update(i); } //{1,2,...,20}
for (int i=6; i<=15; i++) { skC.update(i); } //{6,7,...,15}
Union union = Sketches.setOperationBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).buildUnion();
union.union(skA);
union.union(skB);
// ... option to continue to iterate on the input sketches to union
CompactSketch unionSk = union.getResult(); //the result union sketch
double est = Math.round(unionSk.getEstimate());
System.out.println("A U B : " + est); //the estimate of union
assertEquals(est, 20.0);
//Intersection is similar
Intersection inter = Sketches.setOperationBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).buildIntersection();
inter.intersect(unionSk);
inter.intersect(skC);
// ... option to continue to iterate on the input sketches to intersect
CompactSketch interSk = inter.getResult(); //the result intersection sketch
est = Math.round(interSk.getEstimate());
System.out.println("(A U B) ^ C: " + est); //the estimate of intersection
assertEquals(est, 10.0);
//The AnotB operation is a little different as it is stateless and not iterative:
AnotB aNotB = Sketches.setOperationBuilder().setNominalEntries(k).buildANotB();
CompactSketch diff = aNotB.aNotB(skA, skC);
est = Math.round(diff.getEstimate());
System.out.println("A \\ C : " + est); //the estimate of AnotB
assertEquals(est, 5.0);
}
}
/* OUTPUT:
A U B : 20.0
(A U B) ^ C: 10.0
A \ C : 5.0
*/